Skin wound healing and tissue regeneration
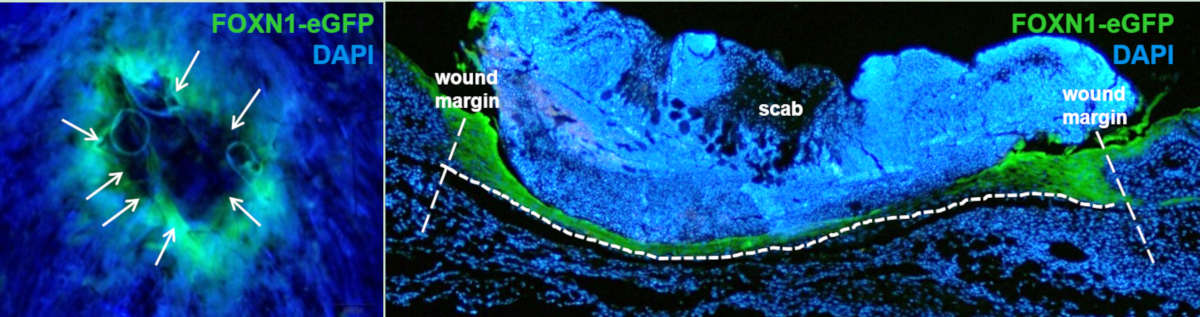
Neotenic phenomenon in gene expression in the skin of Foxn1- deficient (nude) mice – a projection for regenerative skin wound healing
Foxn1 in Skin Development, Homeostasis and Wound Healing
Animal Models of Skin Regeneration 1
Animal Models of Skin Regeneration 2
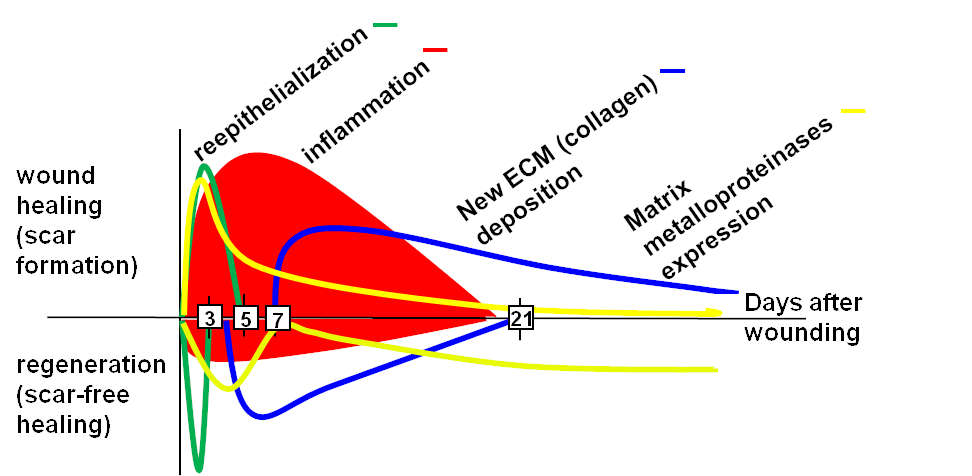
Scarless skin wound healing in FOXN1 deficient (nude) mice is associated with distinctive matrix metalloproteinase expression
Matrix metalloproteinase 9 (MMP-9) is upregulated during scarless wound healing in athymic nude mice
Scarless skin repair in immunodeficient mice
Regeneration in the Ears of Immunodeficient Mice: Identification and Lineage Analysis of Mesenchymal Stem Cells
Foxn1 in epidermal and dermal regulatory pathway
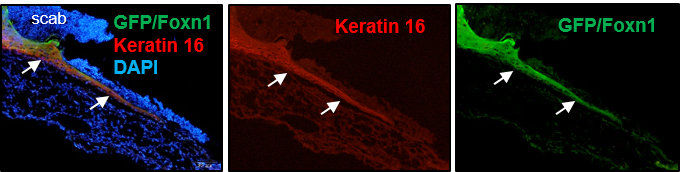
Wnt signaling and the transcription factor Foxn1 contribute to cutaneous wound repair in mice
Foxn1 Control of Skin Function
The Transcription Factor FOXN1 Regulates Skin Adipogenesis and Affects Susceptibility to Diet-Induced Obesity
Foxn1 expression in keratinocytes is stimulated by hypoxia: further evidence of its role in skin wound healing
Neotenic phenomenon in gene expression in the skin of Foxn1- deficient (nude) mice – a projection for regenerative skin wound healing
Effect of TGFβ1, TGFβ3 and keratinocyte conditioned media on functional characteristics of dermal fibroblasts derived from reparative (Balb/c) and regenerative (Foxn1 deficient; nude) mouse models
Foxn1 Transcription Factor Regulates Wound Healing of Skin through Promoting Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition
Cyclosporin A reduces matrix metalloproteinases and collagen expression in dermal fibroblasts from regenerative FOXN1 deficient (nude) mice
Foxn1 in dWAT development and differentiation
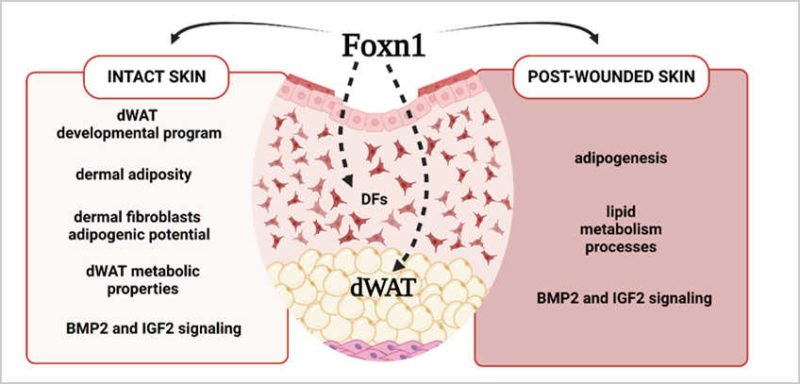
Dermal White Adipose Tissue (dWAT) Is Regulated by Foxn1 and Hif-1α during the Early Phase of Skin Wound Healing
The Transcription Factor FOXN1 Regulates Skin Adipogenesis and Affects Susceptibility to Diet-Induced Obesity
Age, Diet and Epidermal Signaling Modulate Dermal Fibroblasts’ Adipogenic Potential
Age, sex and obesity in skin homeostasis
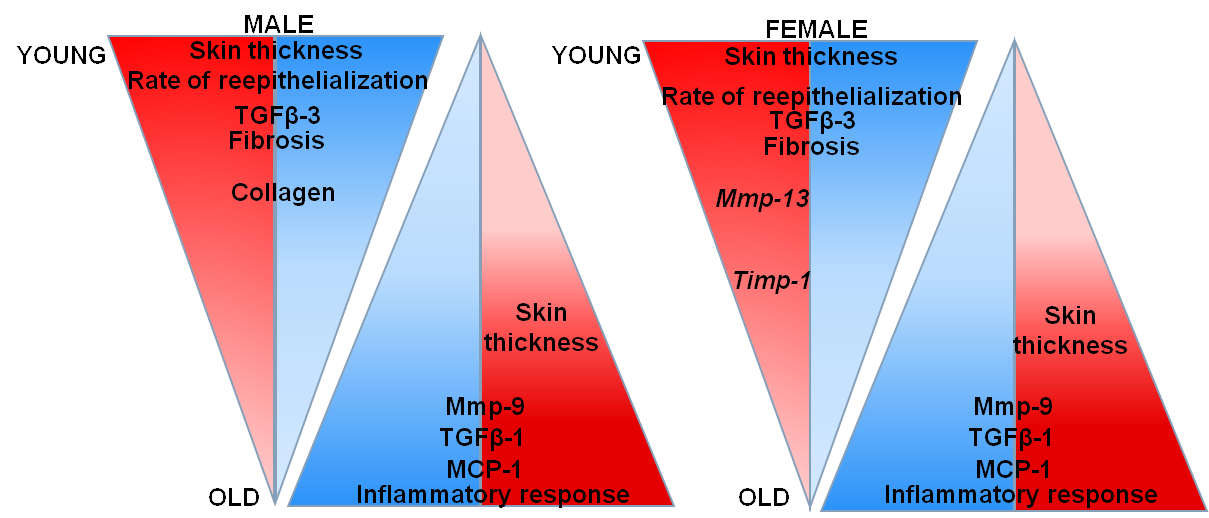
The Transcription Factor FOXN1 Regulates Skin Adipogenesis and Affects Susceptibility to Diet-Induced Obesity
Age, Diet and Epidermal Signaling Modulate Dermal Fibroblasts’ Adipogenic Potential
Cutaneous wound healing in aged, high fat diet-induced obese female or male C57BL/6 mice
Foxn1 and Mmp-9 expression in intact skin and during excisional wound repair in young, adult, and old C57Bl/6 mice
Hypoxia reveals a new function of Foxn1 in the skin
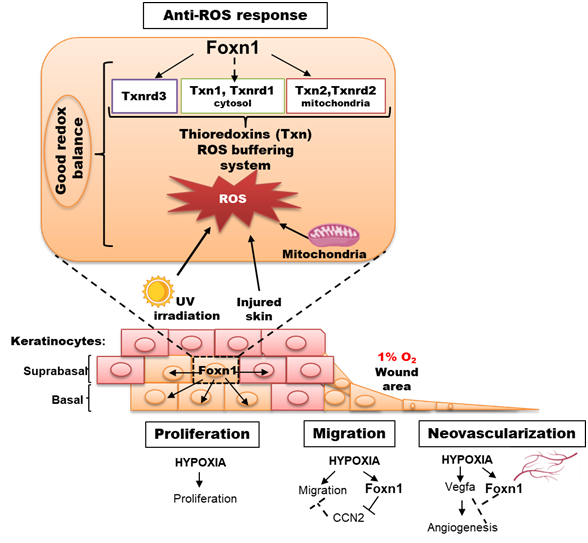
Hypoxia reveals a new function of Foxn1 in the keratinocyte antioxidant defense system
Impairment of the Hif-1α regulatory pathway in Foxn1-deficient (Foxn1−/−) mice affects the skin wound healing process
Foxn1 expression in keratinocytes is stimulated by hypoxia: further evidence of its role in skin wound healing
Adult stem cells in skin homeostasis and therapy
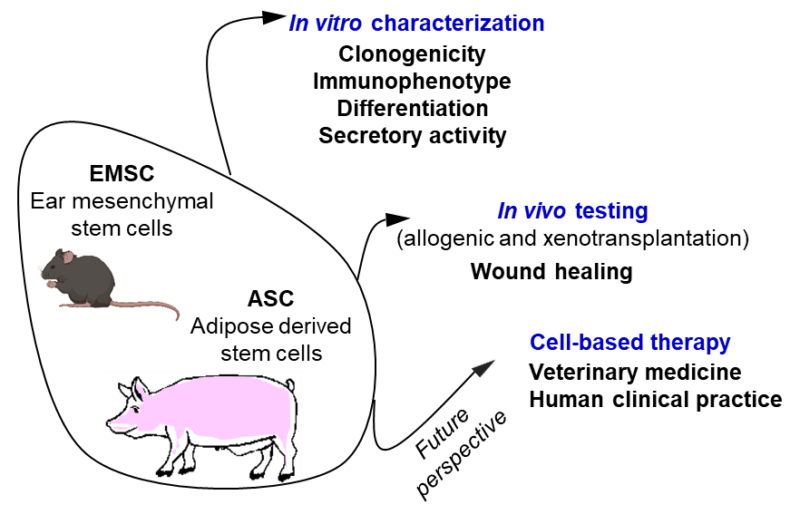
Comparative studies on the effect of pig adipose-derived stem cells (pASCs) preconditioned with hypoxia or normoxia on skin wound healing in mice
Mesenchymal stem cells from the outer ear: a novel adult stem cell model system for the study of adipogenesis
Ear mesenchymal stem cells (EMSC) can differentiate into spontaneously contracting muscle cells
Stem Cell Antigen-1-Positive Ear Mesenchymal Stem Cells Display Enhanced Adipogenic Potential
Cell Growth Characteristics, Differentiation Frequency, and Immunophenotype of Adult Ear Mesenchymal Stem Cells
Reprogramming mouse ear mesenchymal stem cells (EMSC) expressing the Dlk1-Dio3 imprinted gene cluster
Preparation and Differentiation of Mesenchymal Stem Cells from Ears of Adult Mice
Scarless skin repair in immunodeficient mice
Regeneration in the Ears of Immunodeficient Mice: Identification and Lineage Analysis of Mesenchymal Stem Cells
The effect of hypoxia on the proteomic signature of pig adipose-derived stromal/stem cells (pASCs)
Effect of Pig-Adipose-Derived Stem Cells’ Conditioned Media on Skin Wound-Healing Characteristics In Vitro
Adipose-Derived Stromal/Stem Cells from Large Animal Models: from Basic to Applied Science