Skin wound healing and tissue regeneration
Foxn1 in Skin Development, Homeostasis and Wound Healing
Animal Models of Skin Regeneration 1
Animal Models of Skin Regeneration 2
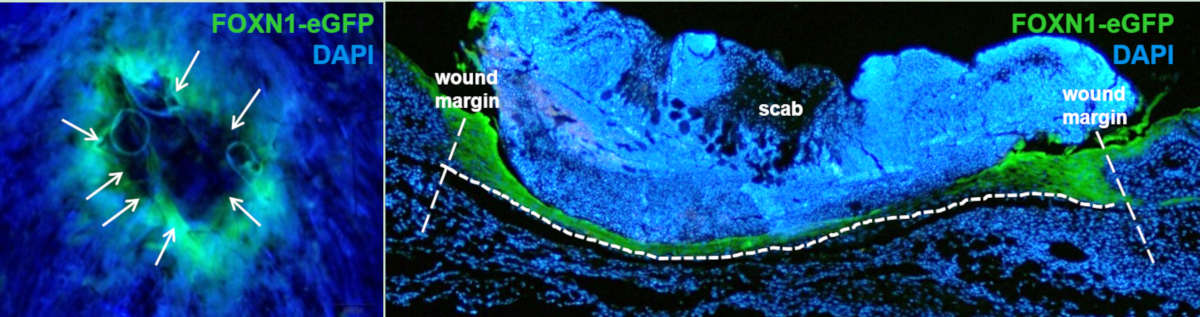
Matrix metalloproteinase 9 (MMP-9) is upregulated during scarless wound healing in athymic nude mice
Scarless skin repair in immunodeficient mice
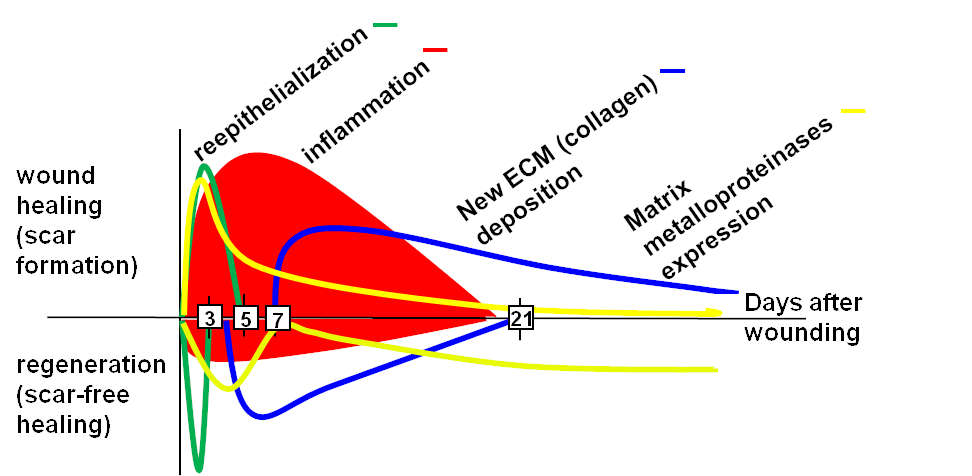
Foxn1 in epidermal and dermal regulatory pathway
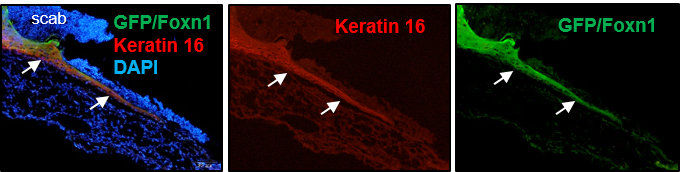
Wnt signaling and the transcription factor Foxn1 contribute to cutaneous wound repair in mice
Foxn1 Control of Skin Function
Foxn1 in dWAT development and differentiation
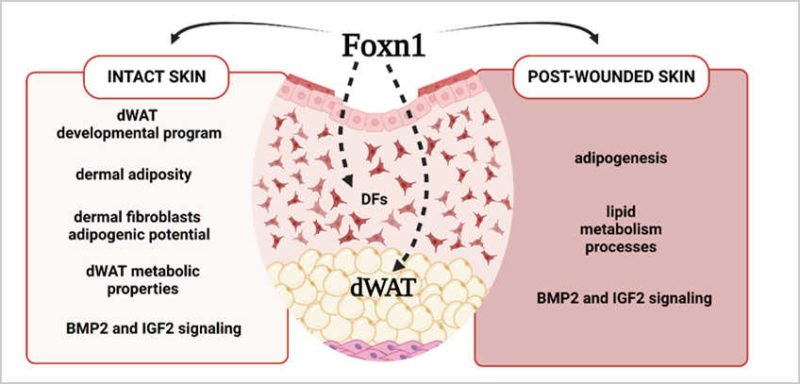
Age, Diet and Epidermal Signaling Modulate Dermal Fibroblasts’ Adipogenic Potential
Age, sex and obesity in skin homeostasis
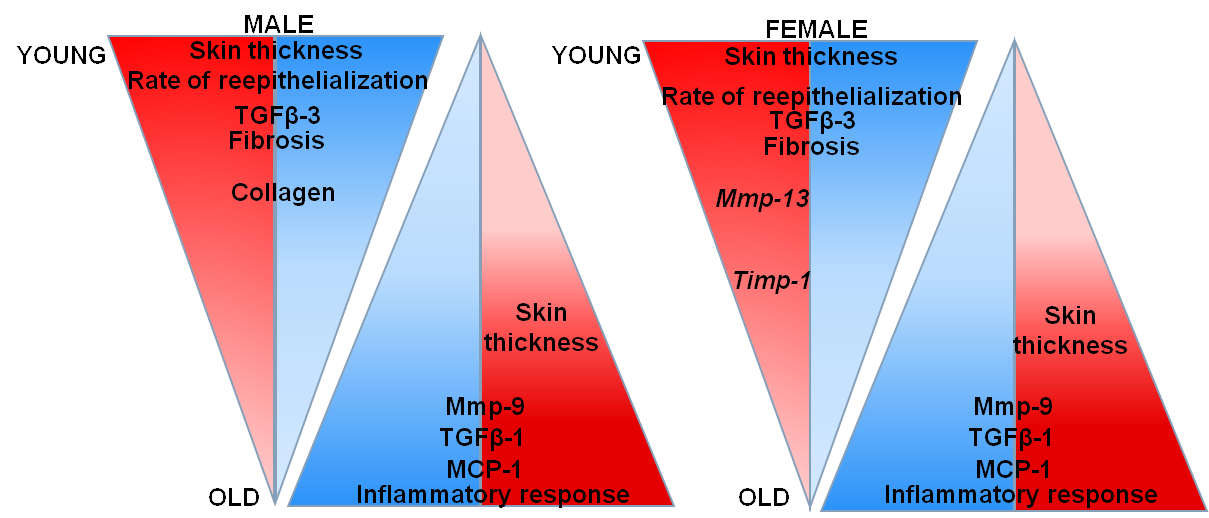
Age, Diet and Epidermal Signaling Modulate Dermal Fibroblasts’ Adipogenic Potential
Cutaneous wound healing in aged, high fat diet-induced obese female or male C57BL/6 mice
Hypoxia reveals a new function of Foxn1 in the skin
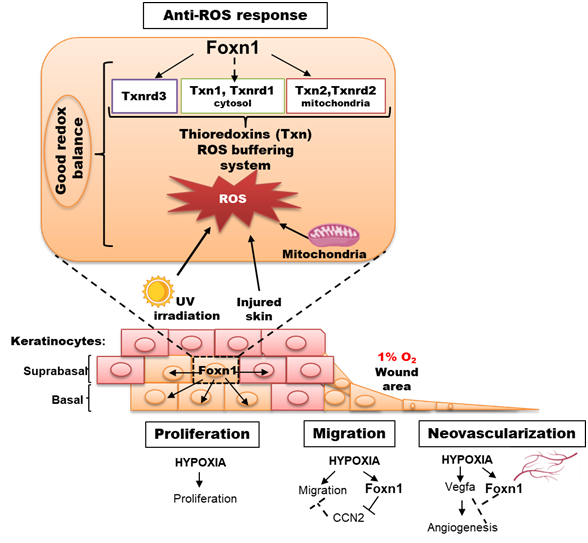
Hypoxia reveals a new function of Foxn1 in the keratinocyte antioxidant defense system
Adult stem cells in skin homeostasis and therapy
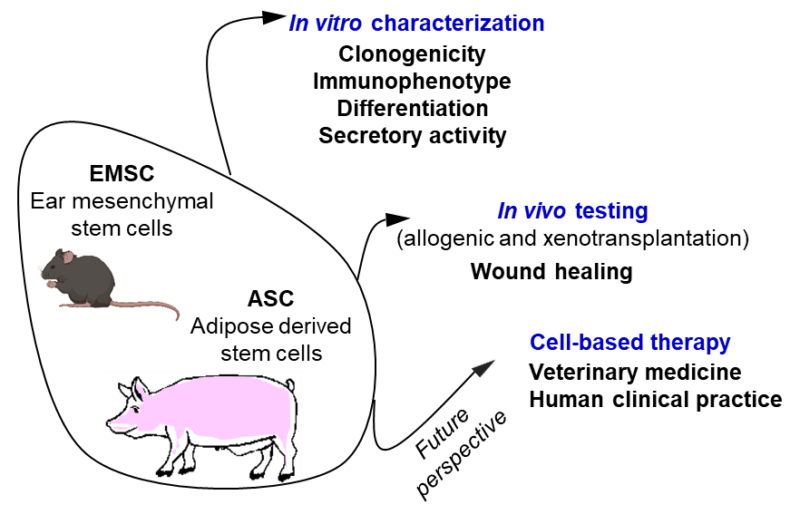
Ear mesenchymal stem cells (EMSC) can differentiate into spontaneously contracting muscle cells
Stem Cell Antigen-1-Positive Ear Mesenchymal Stem Cells Display Enhanced Adipogenic Potential
Preparation and Differentiation of Mesenchymal Stem Cells from Ears of Adult Mice
Scarless skin repair in immunodeficient mice
The effect of hypoxia on the proteomic signature of pig adipose-derived stromal/stem cells (pASCs)
Adipose-Derived Stromal/Stem Cells from Large Animal Models: from Basic to Applied Science